
|
|
ABSOLUTE POVERTY LEVEL: The amount of income a person or family needs to purchase an absolute amount of the basic necessities of life. These basic necessities are identified in terms of calories of food, BTUs of energy, square feet of living space, etc. The problem with the absolute poverty level is that there really are no absolutes when in comes to consuming goods. You can consume a given poverty level of calories eating relatively expensive steak, relatively inexpensive pasta, or garbage from a restaurant dumpster. The income needed to acquire each of these calorie "minimums" vary greatly. That's why some prefer a relative poverty level.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           MARGINAL PHYSICAL PRODUCT: The change in the quantity of total physical product resulting from a unit change in a variable input, keeping all other inputs unchanged. Marginal physical product, usually abbreviated MPP, is found by dividing the change in total physical product by the change in the variable input. Marginal physical product, which more often goes by the name marginal product (MP), is one of two measures derived from total physical product. The other is average physical product. Marginal physical product is the extra output generated by an extra input. Marginal physical product usually goes by the shorter name marginal product. The longer name, created by inserting the word "physical" between "marginal" and "product," serves to distinguish marginal PHYISCAL product from marginal REVENUE product. When no distinction is needed, the term marginal product is suitable.However, when analysis turns to marginal productivity theory and factor markets, a distinction IS important. In particular, marginal revenue product provides a direct link to factor demand. The formula for specifying and calculating marginal physical product from total physical product is given as: | marginal physical product | = | change in total physical product
change in variable input |
The proper economic interpretation of marginal physical product is as the contribution of the last unit of variable input to total production. That is, how much does total product change by adding the last unit? If, for example, the marginal physical product of labor is 25 tacos, then this means that employing the last worker causes total product to increase by 25 tacos. Does this mean the last worker personally produces 25 tacos? No, not at all. Or at least, not necessarily. It means that having this person employed by the firm causes total product to increase by 25 tacos. More often that not, this added worker makes existing workers more productive. Marginal Taco ProductionThe table at the right summarizes the hourly production by Waldo's TexMex Taco World of Super Deluxe TexMex Gargantuan Tacos (with sour cream and jalapeno peppers). The total product numbers presented can be used to derive the marginal product.| Marginal Taco Product | 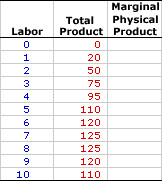 |
The leftmost column is the variable input, specifically the number of workers employed by Waldo's TexMex Taco World, which ranges from 0 to 10. The middle column is the total product, the total number of TexMex Gargantuan Tacos produced each hour, which ranges from a low of 0 to a high of 125 before declining to 110. Keep in mind that the taco production from these workers depends on a given amount of fixed inputs, Waldo's TexMex Taco World restaurant and all of the capital that goes with it.Missing from this table is any mention of marginal physical product. This apparent oversight can be rectified with a few button clicks. - First, consider this question: What is the contribution of the first worker to total Gargantuan Taco production? Or put another way: What is the change in total product resulting from a change in the variable input?
To answer these questions, note that total hourly Gargantuan Taco production with zero workers is also zero. No input, no output. But with one worker busily making Gargantuan Tacos, the hourly taco production increases to 20. The change in total product resulting from the employment of the first worker is 20. Click the [First] button to verify that the marginal physical product of the first worker is 20 tacos.
- How about the marginal physical product of the second worker? A click of the [Second] button reveals that employing the second worker adds 30 Gargantuan Tacos to the hourly taco production of Waldo's TexMex Taco World. This number is found by taking the difference between total hourly taco production with one worker (20 Gargantuan Tacos) and the total hourly taco production with two workers (50 Gargantuan Tacos).
- Now consider the marginal physical product of the third worker. Adding a third worker boosts total hourly taco production from the 50 Gargantuan Tacos produced by two workers to 75 Gargantuan Tacos produced by three workers. This means that the marginal physical product of the third worker is 25 Gargantuan Tacos.
To display marginal physical products associated with the addition of the remaining workers, click the [Others] button.What interesting and useful information can be derived from this expanded table? - First, the marginal physical product of workers increases for the first two workers, reaching a peak of 30 Gargantuan Tacos, then declines thereafter. The increasing marginal physical product observed for the first few workers illustrates increasing marginal returns and the decreasing marginal physical product observed for all subsequent workers illustrates decreasing marginal returns. Moreover, the decreasing marginal physical product is attributable to the law of diminishing marginal returns, THE key principle underlying marginal productivity theory.
- Second, notice that marginal physical product decreases so much that it becomes zero for the eighth worker and even becomes negative for the ninth and tenth workers. The zero value of marginal physical product for the eighth worker also occurs where the total product has reached its maximum value. Coincidence? Not at all. The peak of the total product curve has a zero slope. Marginal physical product is another term for the slope of the total product curve.
The Marginal Product Curve| Marginal Physical Product Curve | 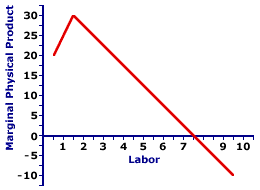 |
The marginal physical product curve is a graphical representation of the relation between marginal physical product and the variable input. The marginal physical product curve for Gargantuan Taco production is displayed to the right.The "general" slope of this curve is negative, with incremental output declining for larger workforces. However, the marginal physical product curve is actually "hump" shaped, with a positive slope giving way to a negative slope. Consistent with the numbers in the table, the curve reaches a peak of 30 Gargantuan Tacos for the second worker. Total and AverageTwo related product measures are total physical product and average physical product.- Total Physical Product: A longer name for total product, this is the total quantity of output produced by a firm for a given quantity of inputs. Total physical product is the foundation upon which the analysis of short-run production for a firm and marginal productivity theory are based. It also provides the basis for calculating marginal physical product.
- Average Physical Product: A longer term for average product, this is the amount of output produced per worker, found by dividing the total product by the number of workers. If, for example, Waldo's TexMex Taco World has a staff of 5 that generates a total product of 110 tacos, then average physical product is 22 tacos.

Recommended Citation:MARGINAL PHYSICAL PRODUCT, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: October 30, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
WHITE GULLIBON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time strolling around a discount warehouse buying club seeking to buy either a black duffle bag with velcro closures or any book written by Isaac Asimov. Be on the lookout for the happiest person in the room.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Two and a half gallons of oil are needed to produce one automobile tire.
|

|
|
"Anyone who has never made a mistake has never tried anything new. " -- Albert Einstein, physicist
|

|
BNA
Bureau of National Affairs
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


