
|
|
ADVERTISING: Information provided about a product by a company to promote or maintain sales, revenue, and or profit. Advertising is often an explicit method of signalling that sellers use to provide information to buyers. The primary objective of advertising from the sellers perspective is to increase (or at least maintain) demand for a product. To accomplish this objective advertising provides buyers with two important types of information -- prices and product quality.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           SHUTDOWN RULE: A rule stating that a firm minimizes economic loss by producing no output in the short run if price is less than average variable cost. This is one of three short-run production alternatives facing a firm. The other two are profit maximization (if price exceeds average total cost) and loss minimization (if price is less than average total cost but greater than average variable cost). | Production Alternatives | | Price and Cost | Result |
|---|
| P > ATC | Profit Maximization | | ATC > P > AVC | Loss Minimization | | P < AVC | Shutdown |
The shutdown rule applies to a firm that is incurring a short-run economic loss that exceeds total fixed cost. This occurs if the price received is less than average variable cost. It is not an absolute rule so much as it is an alternative that any profit maximizing firm is inclined to pursue given production cost and market conditions.Shutting down is one of three short-run production alternatives facing a firm. All three are displayed in the table to the right. The other two are profit maximization and loss minimization. - With profit maximization, price exceeds average total cost at the quantity that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost. In this case, the firm generates an economic profit.
- With loss minimization, price exceeds average variable cost but is less than average total cost at the quantity that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost. In this case, the firm incurs a smaller loss by producing some output than by not producing any output.
In the short run, a firm incurs total fixed cost whether or not it produces any output. As such, if the market price falls below average total cost, it must decide if the economic loss from producing the quantity of output that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost is more or less than the economic loss incurred with shutting down production in the short run (which is equal to total fixed cost).| Shutting Down | 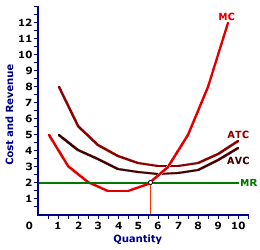 |
The key criterion for this decision is price relative to average variable cost. - If price is less than average variable cost, a firm does not receive enough revenue to pay variable cost let alone any part of fixed cost. As such, the economic loss of operating is GREATER than total fixed cost. A firm is better off shutting down production in the short run, producing zero output, and awaiting a higher price.
- If price is greater than average variable cost, a firm receives sufficient revenue to pay ALL variable cost plus some fixed cost. As such, the economic loss is LESS than total fixed cost. A firm is better off producing the quantity that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost than producing no output, receiving no revenue and incurring a loss equal to total fixed cost.
The exhibit here illustrates the shutdown situation that exists for a hypothetical perfectly competitive firm, Phil the zucchini-growing gardener. The going market price (marginal revenue) of $2 per pound of zucchinis received by Phil, intersects the marginal cost curve at less than the average variable cost curve.Because price falls short of average variable cost, Phil incurs a loss. However, because the price is less than average variable cost, Phil incurs a smaller loss by shutting down production and incurring the loss of total fixed cost, than by producing any output.

Recommended Citation:SHUTDOWN RULE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: October 30, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BROWN PRAGMATOX
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time flipping through mail order catalogs wanting to buy either a key chain with a built-in flashlight and panic button or a green and yellow striped sweater vest. Be on the lookout for bottles of barbeque sauce that act TOO innocent.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
In the early 1900s around 300 automobile companies operated in the United States.
|

|
|
"Anyone who has never made a mistake has never tried anything new. " -- Albert Einstein, physicist
|

|
KSE
Korea Stock Exchange
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


