
|
|
YIELD: The rate of return on a financial asset. In some simple cases, the yield on a financial asset, like commercial paper, corporate bond, or government security, is the asset's interest rate. However, as a more general rule, the yield includes both the interest earned from an asset plus any changes in the asset's price. Suppose, for example, that a $100,000 bond has a 10 percent interest rate, such that the holder receives $10,000 interest per year. If the price of the bond increases over the course of the year from $100,000 to $105,000, then the bond's yield is greater than 10 percent. It includes the $10,000 interest plus the $5,000 bump in the price, giving a yield of 15 percent. Because bonds and similar financial assets often have fixed interest payments, their prices and subsequently yields move up and down as economic conditions change.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           MARGINAL FACTOR COST CURVE, MONOPSONY: A curve that graphically represents the relation between marginal factor cost incurred by a monopsony for hiring an input and the quantity of input employed. A profit-maximizing monopsony hires the quantity of input found at the intersection of the marginal factor cost curve and marginal revenue product curve. The marginal factor cost curve for a monopsony with market control is positively sloped and lies above the average factor cost curve. Monopsony is a market structure with a single buyer or in terms of factor markets, a single employer. This means that monopsony is a price maker with control over the buying side of the market. Market control means monopsony faces a positively-sloped supply curve. To buy a larger quantity, it must pay a higher price.The marginal factor cost curve reflects the degree of market control held by a firm. For a perfectly competitive firm with no market control, the marginal factor cost curve is a horizontal line. For firms with more market control, especially monopsony, the marginal factor cost curve is positively sloped and lies above the average factor cost curve. Marginal Factor Cost Curve,
Monopsony | 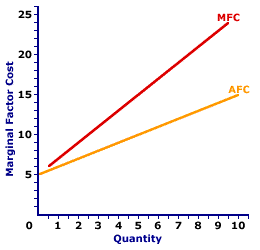 |
The marginal factor cost curve (MFC) for OmniKing Island Resort is displayed in the exhibit to the right. Key to this curve is that OmniKing is a monopsony buyer of workers and thus faces a positively-sloped supply curve. Larger quantities of input can be had only with higher prices.The vertical axis measures marginal factor cost and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of input (workers). Although quantity on this particular graph stops at 10 workers, it could go higher. This curve indicates that if OmniKing hires the first worker, then marginal factor cost is $6. Alternatively, if it hires the tenth worker, then marginal factor cost is $24. For reference, the factor supply curve (and average factor cost curve, AFC) is also presented in the exhibit. The key observation is that the positively-sloped marginal factor cost curve (MFC) lies above the supply curve (AFC) facing OmniKing for hiring labor. The positioning of the marginal factor cost curve above the average factor cost curve reflects the mathematical relation between an average and a marginal. Although this marginal factor cost curve is based on the employment activity of OmniKing Island Resort, a well-known monopsony firm, it works for any buyer with market control. Monopsonistic competition and oligopsony firms that also face positively-sloped supply curves generate comparable marginal factor cost curves.

Recommended Citation:MARGINAL FACTOR COST CURVE, MONOPSONY, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: April 28, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
ORANGE REBELOON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time searching for a specialty store trying to buy either a rechargeable battery for your computer or shoe laces for your snow boots. Be on the lookout for gnomes hiding in cypress trees.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Lewis Carroll, the author of Alice in Wonderland, was the pseudonym of Charles Dodgson, an accomplished mathematician and economist.
|

|
|
"The roots of education are bitter, but the fruit is sweet." -- Aristotle
|

|
OSHA
Occupational Safety and Health Administration
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


