
|
|
NET EXPORTS LINE: The graphical depiction of the relation between net exports and national income (or gross domestic product) that plays a role in Keynesian economics and the Keynesian cross. The net exports line is derived by combining the exports line, relating exports and national income, with the imports line, relating imports and national income. Because exports are largely independent of national income and imports (which are subtracted from exports) increase with national income, the net exports line has a negative slope. The slope of the net exports line is thus the negative of the marginal propensity to import. The aggregate expenditures line used in the Keynesian cross is obtained by adding this net exports line, as well as, government purchases and net exports, to the consumption line. The government purchases line is also combined with investment expenditures for the Keynesian saving-investment model.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           SHORT-RUN AGGREGATE SUPPLY AND MARKET SUPPLY: The short-run aggregate supply curve, or SRAS curve, has similarities to, but differences from, the standard market supply curve. Both are positively sloped. Both relate price and quantity. However, the market supply curve is positively sloped due to the law of diminishing marginal returns and the short-run aggregate supply curve is positively-sloped due to inflexible prices, the pool of natural unemployment, and imbalances in real resource prices. | Two Similar Curves | 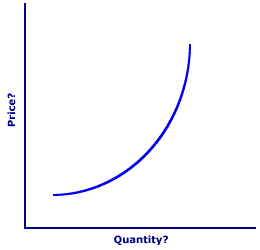 |
To illustrate the specific short-run aggregate supply and market supply curve similarities and differences consider the graph of a positively sloped curve displayed here. Is this a market supply curve or an short-run aggregate supply curve? A cursory analysis suggests that it could be either.To reveal the similarities between the both curves, click the [Market Supply] and [Aggregate Supply] buttons. Doing so illustrates that both curves are positively sloped, with each virtually overlaying the other. Consider the differences between these two curves. - First, note that for the market supply curve, the vertical axis measures supply price and the horizontal axis measures quantity supplied. For the short-run aggregate supply curve, however, the vertical axis measures the price level (GDP price deflator) and the horizontal axis measures real production (real GDP).
- Second, the positive slope of the market curve reflects the law of supply and is attributable to the law of diminishing marginal returns. In contrast, the positive slope of the short-run aggregate supply curve is attributable to: (1) inflexible resource prices that often makes it easier to reduce aggregate real production and resource employment when the price level falls, (2) the pool of natural unemployment, consisting of frictional and structural unemployment, that can be used temporarily to increase aggregate real production when the price level rises, and (3) imbalances in the purchasing power of resource prices that can temporarily entice resource owners to produce more or less aggregate real production than they would at full employment. Similar, but different.
Most notable, the differences between market supply and short-run aggregate supply means that it is not possible to merely add up, or aggregate, the market supply curves for the thousands of goods produced in the economy to derive the short-run aggregate supply curve. The short-run aggregate supply curve dances to its own music and plays be its own set of rules.

Recommended Citation:SHORT-RUN AGGREGATE SUPPLY AND MARKET SUPPLY, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: May 13, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
GRAY SKITTERY
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time surfing the Internet looking to buy either a wall poster commemorating the 2000 Presidential election or a rechargeable flashlight. Be on the lookout for fairy dust that tastes like salt.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The wealthy industrialist, Andrew Carnegie, was once removed from a London tram because he lacked the money needed for the fare.
|

|
|
"We can't take any credit for our talents. It's how we use them that counts. " -- Madeleine L'Engle, Writer
|

|
DW
Durbin-Watson
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


