
|
|
COASE THEOREM: A policy proposition, developed by Ronald Coase, that pollution and other externalities can be efficiently controlled through voluntary negotiations among the affected parties (polluters and those harmed by pollution). A key to the Coase theorem is that many pollution problems involve common-property goods that have no clear-cut ownership or property rights. With clear-cut property rights, "owners" would have the incentive to achieve an efficient level of pollution. This theorem states that it doesn't matter who receives the property rights, so long as someone does. Pollution can be reduced through voluntary negotiation by assigning private property rights to common-property resources. If common-property resources are privately owned, a market in property rights can be established. Owners then have the incentive to protect the quality of their resources.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           TOTAL REVENUE, MONOPOLY: The revenue received by a monopoly firm for the sale of its output. Total revenue is one two bits of information a monopoly firm needs to calculate economic profit, the other is total cost. In general, total revenue is price times quantity--the price received for selling a good times the quantity of the good sold at that price. For a monopoly firm, that charges different prices for different quantities, total revenue increases then decreases. Two other revenue measures directly related to total revenue are average revenue and marginal revenue. Total revenue is often depicted as a total revenue curve. Total revenue is important to the analysis a monopoly firm's short-run production decision. A monopoly firm generally seeks to produce the quantity of output that maximizes profit, which is the difference between total revenue and total cost.Total revenue can be represented in a table or as a curve. For a monopoly firm, the total revenue curve is a "hump-shaped" curve the emerges from the origin, reaches a peak, then subsequently falls. The total revenue received by a firm is price times quantity, often expressed as this simple equation: | total revenue | = | price | x | quantity |
For a monopoly firm that is a price maker rather than price taker, market control means the firm faces a negatively-sloped demand curve. As such, the price received is not fixed, but depends on the quantity of output sold.Total Revenue,
Medicine Style | 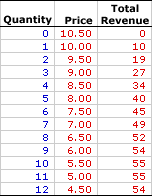 |
The table to the right summarizes the total revenue received by a hypothetical monopoly firm, Feet-First Pharmaceutical. This firm owns the patent to Amblathan-Plus, the only cure for the deadly foot ailment known as amblathanitis. As the only producer of Amblathan-Plus, Feet-First Pharmaceutical is a monopoly with extensive market control, facing a negatively-sloped demand curve. To sell a larger quantity of Amblathan-Plus, Feet-First Pharmaceutical must lower the price.Consider a few tidbits of information about total revenue for a firm with market control. - First, total revenue is zero if Feet-First Pharmaceutical sells no medicine. This makes sense. If nothing is sold, no revenue is received.
- Second, the price changes with the quantity of output sold. Feet-First Pharmaceutical can sell 1 ounce of medicine for $10 per ounce. However, if it choses to sell 5 ounces, then it must lower the price to $8 per ounce.
- Third, as Feet-First Pharmaceutical sells more medicine it receives more total revenue... UP TO A POINT. While total revenue received by Feet-First Pharmaceutical increases for the first 10 ounces sold, it declines for the 12th ounce.
- Fourth and last, the extra revenue generated for selling more medicine is not constant nor is it equal to the price. For example, the 5th ounce of medicine adds a extra $6 of revenue even though the price is $8.
Total Revenue Curve,
Medicine Style | 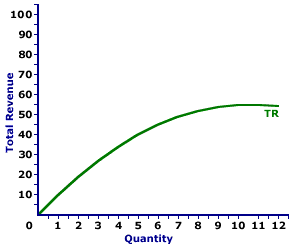 |
The total revenue curve for a monopoly firm with market control is "humped shaped." The total revenue curve for Feet-First Pharmaceutical is displayed in the exhibit to the right. Key to this curve is that Feet-First Pharmaceutical is a monopoly provider of a drug called Amblathan-Plus and thus faces a negatively-sloped demand curve. Larger quantities of output are only possible with lower prices.The vertical axis measures total revenue and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of output (ounces of medicine). Although quantity on this particular graph stops at 12 ounces of medicine, it could go higher. This curve indicates that if Feet-First Pharmaceutical sells 1 ounce of medicine (at $10 per ounce), then it receives $10 of total revenue. Alternatively, if it sells 10 ounces (at $5.50 per ounce), then it receives $55 of total revenue. Should it sell 12 ounces (at $4.50 per ounce), then it receives only $54 of total revenue. For Feet-First Pharmaceutical the total revenue "curve" actually is a "curve." The slope of this curve falls as more output is produced, eventually reaching a peak, then becoming negative. The changing slope of this curve is due to the changing price. Although this total revenue curve, and preceding table of total revenue numbers, is based on the production activity of Feet-First Pharmaceutical, a well-known monopoly firm, it could also be for any firm with market control. Monopolistic competition and oligopoly firms that also face negatively-sloped demand curves generate comparable total revenue.

Recommended Citation:TOTAL REVENUE, MONOPOLY, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: April 29, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | |
Related Websites (Will Open in New Window)... | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BLACK DISMALAPOD
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time at the confiscated property police auction seeking to buy either handcrafted decorations to hang on your walls or throw pillows for your bed. Be on the lookout for slightly overweight pizza delivery guys.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
In the early 1900s around 300 automobile companies operated in the United States.
|

|
|
"Something in human nature causes us to start slacking off at our moment of greatest accomplishment. As you become successful, you will need a great deal of self-discipline not to lose your sense of balance, humility and commitment." -- H. Ross Perot
|

|
AMW
Average Monthly Wage
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


